About us
Beijing JWGB Instrument Co., Ltd.
sales@jwgb.net
Copyright 2004–2024 JWGB.NET
 TEL: +86 010 63326036
TEL: +86 010 63326036
 ENAIL:sales@jwgb.net
ENAIL:sales@jwgb.net
Cement is an indispensable and essential material in the construction industry. After hardening, it not only exhibits high strength but also resists erosion from freshwater or saltwater. The quality and characteristics of cement are crucial factors that impact the construction speed, cost of engineering projects, signify milestones in the mutual development of the construction industry and materials field in a country, and are closely related to the safety factor of buildings. Therefore, the quality of cement has garnered widespread attention across various industries.
As the specific surface area of cement is a crucial criterion for evaluating its quality, obtaining accurate data is essential to ensure the quality of construction projects. Hence, this article will compare the principles and characteristics of the Blaine method and the BET nitrogen adsorption method, exploring the most suitable method for specific surface area testing of cement.
Blaine method for measuring specific surface area.
The Blaine method is primarily used to determine the specific surface area of cement and powdered materials with specific surface areas in the range of 0.2 to 0.6 m2/g. However, it is not suitable for porous materials and ultrafine powders. This method is based on the principle that the resistance to the flow of air through a sample layer with a certain porosity and specified thickness changes, causing variations in flow velocity, which is used to measure the specific surface area of the sample.
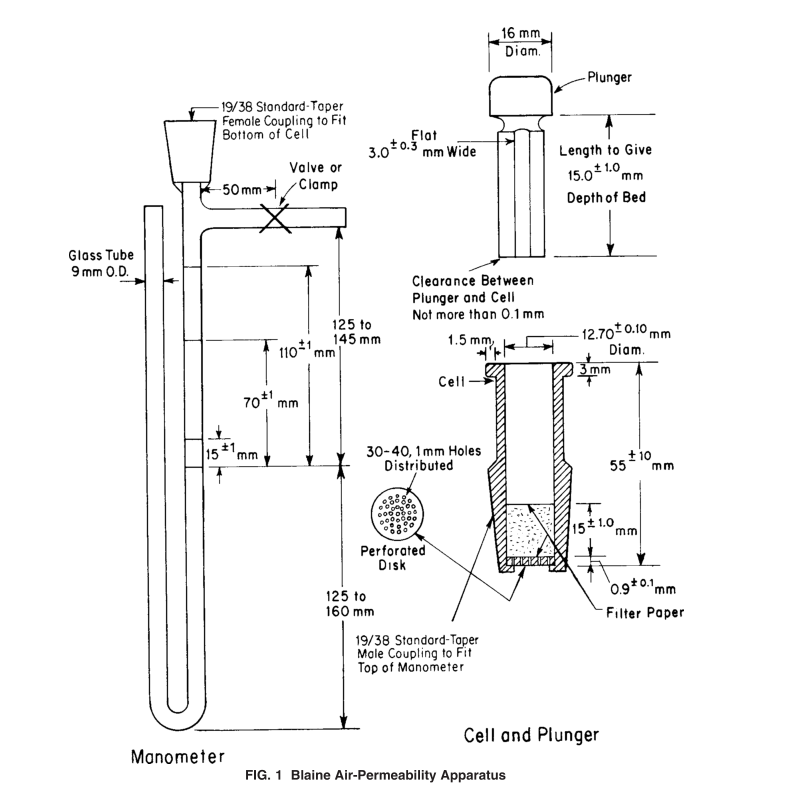
The experimental procedure consists of two main parts. Firstly, the density of the test sample is determined using the Le Chatelier flask method. The porosity of the sample layer in the air permeability apparatus is then adjusted by weights. Secondly, the pre-treated sample is compacted in the permeability apparatus using weights, and the apparatus is tightly connected to the manometer for air permeability testing. The rise and fall of the distilled water meniscus in the manometer indicate changes in pressure, and the relative time taken for the meniscus to pass the first and second graduation lines is recorded.
BET method for measuring specific surface area (low-temperature nitrogen adsorption method).
The BET method is applicable for the determination of specific surface area in powders and porous materials, including nanoscale powders and nanoporous materials, with a measurement range from 0.001 m2/g to 3000 m2/g.
The experimental principle revolves around placing the sample in a gas system, where physical adsorption occurs on the material surface (the surface area of particles externally and internally, as schematically shown in the diagram below) at low temperatures. When adsorption reaches equilibrium, the equilibrium adsorption pressure and the quantity of adsorbed gas are measured. The BET equation is then used to calculate the adsorption amount of the sample's monolayer, thereby determining the specific surface area of the sample.
The methods for measuring specific surface area based on the BET nitrogen adsorption principle can be categorized into static capacity method and dynamic method (gas chromatography flow method), and the corresponding instruments are also classified as static and dynamic.
Through a series of measurements of relative pressure (P/P0) and adsorbed gas volume (V), slopes (A) and intercepts (B) are determined using BET plots or the least squares method. Single-layer capacity and BET parameter C are derived from these values. The C value represents the interaction forces between the adsorbent and adsorbate but cannot be used for quantitative calculations of adsorption heat. When nitrogen is used as the adsorption gas, the intercept is often relatively small compared to the slope, and C value >> 1.
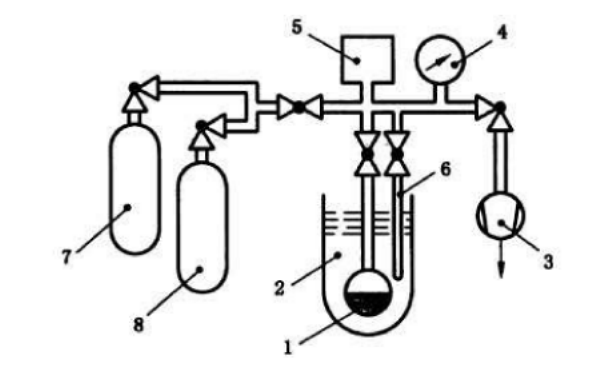

Nitrogen gas is generally considered the most suitable adsorption gas. For samples with low specific surface area, when using nitrogen for measurement, the instrument sensitivity may be insufficient. In such cases, heavier molecules or adsorption gases with vapor pressures lower than nitrogen, such as hydrogen, can be used. Results obtained using different adsorption gases may deviate from each other due to variations in molecular cross-sectional areas, accessible pores, and measurement temperatures. To achieve result repeatability, it is recommended to take multiple samples for repeated measurements and report the average standard deviation.
Comparisons
The Blaine method for measuring specific surface area involves numerous manual measurements and calculations. During the process of measuring specific surface area, the measurement of cement density is crucial. Density determines whether there is any deviation in the measured weight of the cement, which affects the porosity of the cement in the experiment, thereby influencing the results of specific surface area determination. Using the Le Chatelier flask for density measurement requires strict control of constant temperature bath temperature, experimental time, and reading time to minimize reading errors before kerosene volatilization and mass deviation occur. Laboratory conditions during the measurement of cement specific surface area also need to be carefully controlled, with a requirement that the laboratory humidity should not exceed 50%. It is essential to ensure that the liquid level in the manometer is at an appropriate height during the experiment. When the liquid level is too high, the gas flow rate slows down, leading to an overestimation of specific surface area. Conversely, when the liquid level is too low, the gas flow rate increases, resulting in underestimated values.
In contrast, when measuring specific surface area using the BET method, it only requires accurate weighing and double-checking of sample quality. The values are then entered into the software, and the system can perform the calculations. The entire experimental process is computer-controlled, making it not only simple and user-friendly but also maximizing experimental accuracy and minimizing operational errors. For projects such as cement process improvement and incoming material inspection that require a large number of experiments, efficiency and accuracy are essential, and the advantages of the BET method for measuring specific surface area are self-evident.
【Recommended】