About us
Beijing JWGB Instrument Co., Ltd.
sales@jwgb.net
Copyright 2004–2024 JWGB.NET
 TEL: +86 010 63326036
TEL: +86 010 63326036
 ENAIL:sales@jwgb.net
ENAIL:sales@jwgb.net
In the field of electric vehicle batteries, ternary lithium and lithium iron phosphate are the two most commonly used types of lithium-ion batteries. Ternary lithium batteries are named "ternary" due to the nickel-cobalt-aluminum or nickel-cobalt-manganese in their cathode materials, while the cathode material of lithium iron phosphate batteries is lithium iron phosphate.
As cobalt, an element in ternary lithium batteries, is a strategic metal, its global supply prices have been soaring consistently. In contrast, lithium iron phosphate batteries do not contain this expensive metal, making them more cost-effective. Consequently, more automotive manufacturers are opting for lithium iron phosphate batteries to reduce production costs and gain a competitive market share.

Considering the future global demand for power batteries and energy storage batteries, it is estimated that by 2025, the global demand for lithium iron phosphate cathode materials will be approximately 980,000 tons, corresponding to a market size of about 28 billion yuan. The large-scale production of lithium iron phosphate is expected to stimulate the market demand for specific surface area analyzers.
As is well known, the specific surface area analyzer has extensive application demands in the lithium-ion battery industry, primarily employed for the specific surface area testing of materials such as positive electrode materials, ternary precursor materials, negative electrode materials, and membrane coatings using aluminum oxide.
In the case of lithium iron phosphate, as a positive electrode material for power batteries, its specific surface area is closely related to the battery's performance. Typically, the specific surface area of lithium iron phosphate is linearly related to its carbon content. During production, specific surface area testing instruments are used for assessment. If the specific surface area is too small, it indicates insufficient carbon coating on the material, directly leading to higher internal resistance and poor cycling performance in the battery. Conversely, if the specific surface area is too large, it suggests an excessive carbon coating on the material, resulting in excellent electrochemical performance but potential issues such as aggregation, difficulties in electrode processing, and uneven coating.
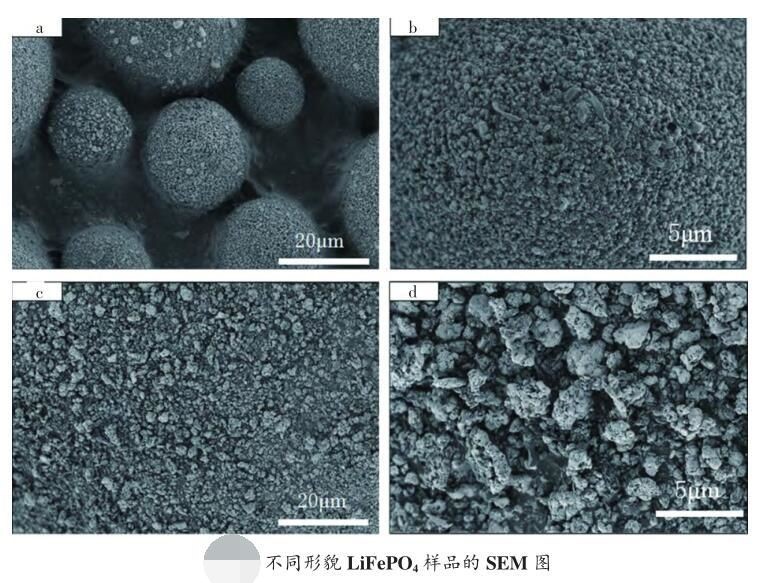

Fast, efficient, and precise testing relies on high-performance testing instruments. The AMI-QUICK 200 series specific surface area analyzer can complete BET testing for four samples within 45 to 60 minutes, making it highly suitable for the online rapid determination in powder production plants.